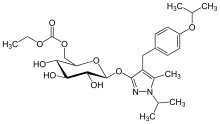
REMOGLIFLOZIN ETABONATE
5-methyl-4-[4-(1-methylethoxy)benzyl]-1-(1-methylethyl)-1H-pyrazol-3-yl 6-O-(ethoxycarbonyl)-β-D-glucopyranoside, CAS 442201-24-3
189075 BHV-091009 GSK-189075 GSK-189075A KGT-1681
BHV Pharma Kissei (Originator) , GlaxoSmithKline
Remogliflozin etabonate (INN/USAN)[1] is a proposed drug for the treatment of type 2diabetes being investigated by GlaxoSmithKline.[2] Remogliflozin is now being developed by BHV Pharma.
Remogliflozin inhibits the sodium-glucose transport proteins, which are responsible for glucose reabsorption in the kidney. Blocking this transporter causes blood glucose to be eliminated through the urine.[3]
- Statement on a nonproprietory name adopted by the USAN council
- Fujimori Y, Katsuno K, Nakashima I, Ishikawa-Takemura Y, Fujikura H, Isaji M (June 2008). “Remogliflozin etabonate, in a Novel Category of Selective Low-Affinity / High-Capacity Sodium Glucose Cotransporter (SGLT2) Inhibitors, Exhibits Antidiabetic Efficacy in Rodent Models”. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 327 (1): 268–276.doi:10.1124/jpet.108.140210. PMID 18583547.
- Prous Science: Molecule of the Month November 2007
DPP IV inhibitors represent a novel class of agents that are being developed for the treatment or improvement in glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. For example, DPP IV inhibitors and their uses are disclosed in WO 2002/068420, WO 2004/018467, WO 2004/018468, WO 2004/018469, WO 2004/041820, WO 2004/046148, WO 2005/051950, WO 2005/082906, WO 2005/063750, WO 2005/085246, WO 2006/027204, WO 2006/029769, WO2007/014886; WO 2004/050658, WO 2004/1 1 1051 , WO 2005/058901 , WO 2005/097798; WO 2006/068163, WO 2007/071738, WO 2008/017670; WO 2007/054201 or WO 2007/128761.

Chemical structures of remogliflozin etabonate (A), remogliflozin (B), sergliflozin (C), phlorizin (D), and T-1095 (E). Remogliflozin etabonate is metabolized to remogliflozin, its active form.