Tianagliflozin,
taigeliejing, 6-deoxydapagliflozin
| Molecular Formula: | C21H25ClO5 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight: | 392.8732 g/mol |
IND Filing…Tianjin Institute of Pharmaceutical research
Tianjin Institute Of Pharmaceutical Research,
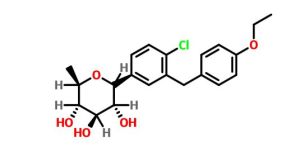
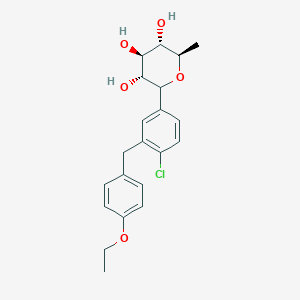
(3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-[4-chloro-3-[(4-ethoxyphenyl)methyl]phenyl]-6-methyloxane-3,4,5-triol
1–[4–Chloro–3–(4–ethoxybenzyl)phenyl]–1,6–dideoxy–β–d–glucopyranose

CAS N. 1461750-27-5
The structures of dapagliflozin and 6-deoxydapagliflozin (1)
,deletion of the 6-OH in the sugar moiety of dapagliflozin led to the discovery of a more potent SGLT2 inhibitor, 6-deoxydapagliflozin (1, ). In an in vitro assay, 1 was a more active SGLT2 inhibitor, with IC 50 = 0.67 nM against human SGLT2 (hSGLT2), as compared with 1.1 nM for dapagliflozin, leading to the identification of 1 as the most active SGLT2 inhibitor discovered so far in this field. Also in an in vivo assay, 1 also introduced more urinary glucose in a rat urinary glucose excretion test (UGE) and exhibited more potent blood glucose inhibitory activity in a rat oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) than dapagliflozin.

SPECTRAL DATA of Tianagliflozin
1 as a white solid (3.65 g, 93 %). R f = 0.35 (EtOAc);
m.p.: 148–149 °C;
1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d 6): δ = 7.35 (d, 1H, J = 8.4 Hz), 7.25 (s, 1H), 7.18 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz), 7.08 (d, 2H, J = 8.4 Hz), 6.81 (d, 2H, J = 8.4 Hz), 4.95 (d, 1H, J = 5.2 Hz, OH), 4.90 (d, 1H, J = 4.4 Hz, OH), 4.79 (d, 1H, J = 5.6 Hz, OH), 3.92–4.01 (m, 5H), 3.24–3.29 (m, 1H), 3.18–3.22 (m, 1H), 3.09–3.15 (m, 1H), 2.89–2.95 (m, 1H), 1.29 (t, 3H, J = 7.0 Hz, CH2 CH 3 ), 1.15 (d, 3H, J = 6.0 Hz, CHCH 3 ) ppm;
13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d 6): δ = 156.85, 139.65, 137.82, 131.83, 131.16, 130.58, 129.52, 128.65, 127.14, 114.26, 80.71, 77.98, 75.77, 75.51, 74.81, 62.84, 37.55, 18.19, 14.62 ppm;
IR (KBr): v¯¯¯ = 3,564 (w), 3,385 (s), 2,981 (s), 2,899 (s), 2,861 (s), 1,613 (m), 1,512 (s), 1,477 (m), 1,247 (s), 1,102 (s), 1,045 (s), 1,012 (s) cm−1;
HR–MS: calcd for C21H29ClNO5 ([M + NH4]+) 410.1729, found 410.1724.
PATENT related
http://www.google.com/patents/WO2013044608A1?cl=en
http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs40242-014-4043-9#/page-1
Design of SGLT2 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes: A History Driven by Biology to Chemistry.
Abstract
A brief history of the design of sodium-dependent glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors is reviewed. The design of O-glucoside SGLT2 inhibitors by structural modification of phlorizin, a naturally occurring O-glucoside, in the early stage was a process mainly driven by biology with anticipation of improving SGLT2/SGLT1 selectivity and increasing metabolic stability. Discovery of dapagliflozin, a pioneering C-glucoside SGLT2 inhibitor developed by Bristol-Myers Squibb, represents an important milestone in this history. In the second stage, the design of C-glycoside SGLT2 inhibitors by modifications of the aglycone and glucose moiety of dapagliflozin, an original structural template for almost all C-glycoside SGLT2 inhibitors, was mainly driven by synthetic organic chemistry due to the challenge of designing dapagliflozin derivatives that are patentable, biologically active and synthetically accessible. Structure-activity relationships (SAR) of the SGLT2 inhibitors are also discussed.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25557661
Paper

Discovery of 6-Deoxydapagliflozin as a Highly Potent Sodium-dependent Glucose Cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitor for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/ben/mc/2014/00000010/00000003/art00009?crawler=true
CLIP
A facile synthesis of 6-deoxydapagliflozin


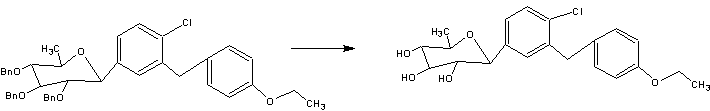
The synthetic route to the target compound 1 is shown in Scheme 3. The starting material methyl 2,3,4-tri-O-benzyl-6-deoxy-6-iodo-α–d-glucopyranoside (3) was prepared from commercially available methyl α–d-glucopyranoside (2) according to a known method [5, 6].
Iodide 3 was reductively deiodinated to give 4 in 91 % yield under hydrogenolytic conditions using 10 % Pd/C as catalyst in the presence of Et3N as base in THF/MeOH at room temperature.
when the iodide 3 was treated with Barton–McCombie reagent (n-Bu3SnH/AIBN) [7] in toluene at room temperature no reaction occurred; however, when the reaction was carried out at elevated temperatures, such as reflux, a complex mixture formed with only a trace amount (3 %, entry 1) of the desired product 4.
When the iodide 3 was treated with LiAlH4 in THF at 0 °C to room temperature, another complex mixture was produced with only a trace amount (2 %, entry 2) of 4.
When Pd(OH)2 was used as the hydrogenolysis catalyst instead of 10 % Pd/C, the desired 4 was indeed formed (14 %, entry 4), but most of the starting material was converted to a few more polar byproducts, which were believed to result from the cleavage of at least one of the benzyl groups.
pdf available
Monatshefte für Chemie – Chemical Monthly
, Volume 144, Issue 12, pp 1903-1910
////////IND Filing, SGLT-2 inhibitor, type 2 diabetes, Tianagliflozin, taigeliejing, 6-deoxydapagliflozin
Clc1c(cc(cc1)C2[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O2)C)O)O)O)Cc3ccc(cc3)OCC